Perimeter Security - 1 -Layers
Defending the Perimeter - 1st Layer:
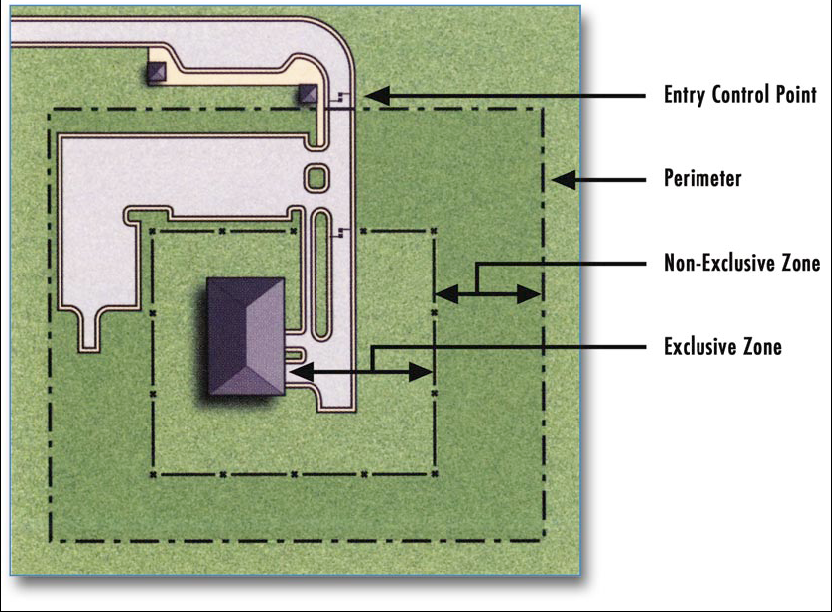
Outermost perimeter is line of demarcation.
- Crossing the boundary establishes intent - marks an aggressor.
- It is the first opportunity to provide detection.
- Usually provides minimal delay.
_______________________________________________________________________
Exclusion Zone - 2nd Layer:
Defined inner perimeter or open space.
- Obstruction free or clear zone.
- Allows detection of aggressors or threats.
- Supports sensor based detection.
Traveling across intermediate space is vulnerability for aggressor and provides delay.
Building Exterior - 3rd Layer:
Depending on level of public access, building exterior may be significant layer of the protective system. It defines the end of site security. The remaining layers are defined within the building as appropriate for the assets within.
Perimeter Security - 2 - Components
2.1 Fencing
Many styles of fencing:
Chainlink
Ornamental
Anti-Climb / High Security
Capabilities:
Most have limited ability to delay penetration
Can be used as a platform for detection sensors
Some can also be helpful in obscuring targets or even predetonating certain standoff weapons
2.2 Vehicle Barrier Systems
Barrier systems are used to defend against the moving vehicle bomb
threat. Of Two types:
Passive
Active
Design is based on capacity to absorb or dissipate kinetic energy of threat vehicle allowing no more than the maximum allowed penetration. Almost all systems are tested to prove performance. You should be weary of using any product that hasnt been tested
2.2.1 Passive Vehicle Barriers
Barrier is stationary and it is designed to prevent the vehicle from penetrating
successfully past barrier.
Sometimes incorporated into perimeter barrier / fence.
Insure Containment of Unscreened or Suspect Vehicles; only permit
access through access points.
Can often use topographical features as passive vehicle barriers.
2.2.2 Active Vehicle Barriers
Selection Based on Required Operational Performance and Site Conditions.
Potential Threat Must be Quantified
Kinetic Energy - I.e. 15,000 lb vehicle at 40 mph
Angle of Approach
Barrier is Selected such that can Absorb the Kinetic Energy While Not Allowing Penetration That Exceeds the Allowable for the Site
Perimeter Security - 3 - Tactics
3.1 Tactic: Vehicle Bombs
Stationary Vehicle Bombs:
With stationary bombs the aggressor doesnt attempt to crash through
barriers
Attempt to get as close the facility as possible with out risking detection
Historically, the most common type of vehicle bomb attack
Moving Vehicle Bombs:
Aggressor is willing to crash through barriers to reach facility
Perimeter defining standoff must be capable of stopping the threat vehicle
For both cases, standoff distance is the best mitigation
For stationary vehicle bomb:
Boundary is defined such that a vehicle crossing boundary draws attention
and initiates response force action
Maximize distance from parking areas
For moving vehicle bomb:
Boundary must resist the vehicle
Determine design speed based on roadway layout
Minimize direct approaches
Define passive and active barriers
3.2 Tactic: Exterior Attack
This tactic is mainly focused on small improvised explosive devices
The site design can incorporate a exclusive standoff zone to keep
aggressors away from the building and limit their ability to place devices near the building or throw devices towards the building
Clear zone can also be provided around the building so that devices are easier to detect.
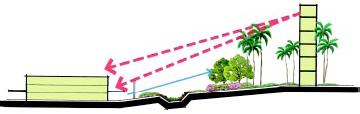
3.3 Tactic: Standoff Weapons
Standoff weapons include mortars, RPGs, and ballistics
Site Design Considerations:
Minimize Vantage Points, locate facility far from vantage points
Consider potential use of predetonation screen (for RPGs) as perimeter
barrier defining standoff if that is applicable tactic
Use of obstruction screens or landscaping to block sightlines

_______________________________________________________________________
3.4 Tactic: Forced Entry
Tactic involves various levels of tools and explosives to attempt to breach the security of the facility.
Site Design Considerations:
Clear zone, avoid features that provide concealment for aggressors
Avoid siting the facility near utility passages that may aid aggressor or
secure the utility access points
Focus on security lighting to support IDS
Provide additional fencing or barrier at facility perimeter if necessary
Significant distance between first detection layer and building causes
delay and exposes aggressor to further detection possibilities
3.5 Tactic: Visual Surveillance, Eavesdropping
Similar to standoff weapons, you want to eliminate or control vantage
points including nearby buildings
Provide clear zone adjacent to buildings so aggressors cant hide near
the building
Consider using perimeter barrier to provide concealment and obscure
assets